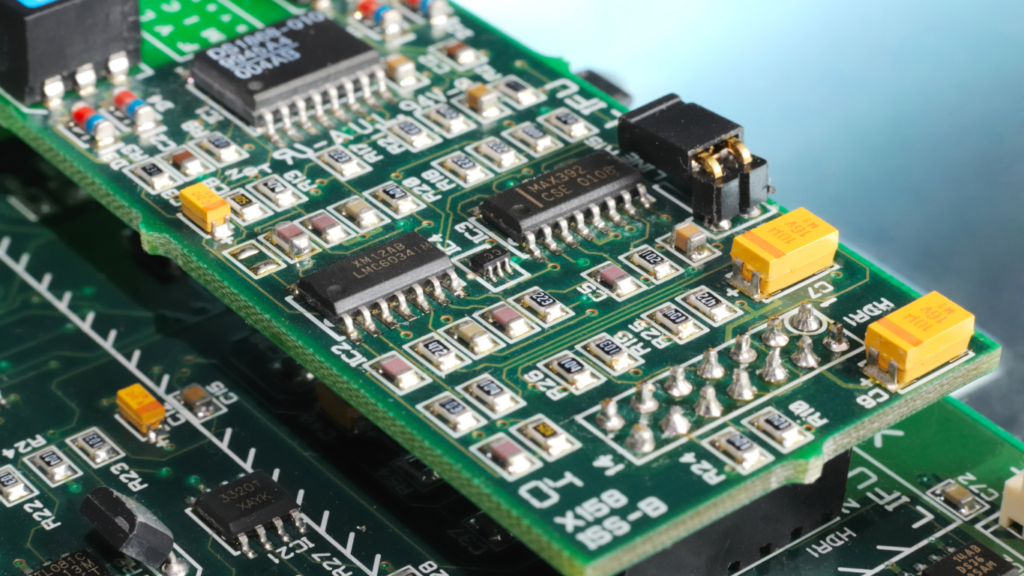
A Double-Sided PCB is a type of printed circuit board where electronic components and conductive traces are placed on both sides of the board. This design allows for more complex and higher-density circuits than single-sided PCBs, offering greater flexibility in terms of component placement and connectivity.
Key Features:
- Two Sides for Components and Traces: Components can be mounted on both the top and bottom surfaces of the PCB, while copper traces are used to connect them on either This allows for more efficient use of space.
- Increased Complexity: Double-sided PCBs are suitable for more intricate circuits that require a higher number of components and connections than single-sided boards.
- Through-Hole and Surface-Mount Components: Double-sided PCBs can accommodate both through-hole and surface-mount technology (SMT), making them versatile for different types of components.
- Higher Density: The use of both sides for component placement and routing allows for denser, more compact designs, which is particularly useful for complex or space-constrained
Applications:
- Consumer Electronics: Many advanced consumer electronics, such as smartphones, computers, and audio systems, use double-sided PCBs to handle more complex circuit
- Automotive Electronics: Double-sided PCBs are used in automotive systems for applications like navigation, control systems, and sensors, where space and performance are critical.
- Industrial Equipment: Machines and equipment that require robust, high-performance circuits—such as robotics, automation systems, and control panels—benefit from double- sided PCBs.
- Medical Devices: More sophisticated medical equipment, such as diagnostic machines and wearable health devices, often require double-sided PCBs for reliable and compact electronic designs.
Advantages:
- Improved Circuit Density: By using both sides of the board, you can fit more components into a smaller area, which is essential for compact devices.
- Better Performance: Double-sided PCBs can handle more complex connections, allowing for faster, more reliable circuit performance.
- Cost-Effective for Complex Designs: While slightly more expensive than single-sided boards, double-sided PCBs are still a cost-effective option for devices that require advanced circuitry without resorting to multi-layer designs.
In summary, double-sided PCBs provide a more flexible and efficient solution for circuits with moderate complexity, offering a balance between performance, size, and cost. They are commonly used in applications where both high circuit density and cost- effectiveness are important.
